Month: March 2017
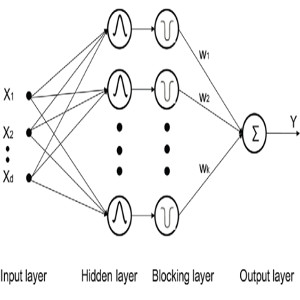
A novel multi-scale regression and classification method
Typically neural network algorithms use either large (e.g. sigmnoidal) or local (e.g. Gaussian) activation functions. Here we propose a new architecture and training method that integrates activation functions from multiple scales while balancing their signal absorption in local and global scales. FUrther information: G. Mountrakis , W. Zhuang+ (2012). Integrating […]
Read More
Biomass estimation using waveform LiDAR signals
Waveform LiDAR offer considerable benefits in large scale biomass estimation. A new algorithm is proposed that uses information from the signal’s vertical structure to estimate more accurately vegetation above ground biomass. Further information: W. Zhuang, G. Mountrakis, J. Wiley, C. Beier (2015). Estimation of Aboveground Forest Biomass Using Metrics Based […]
Read More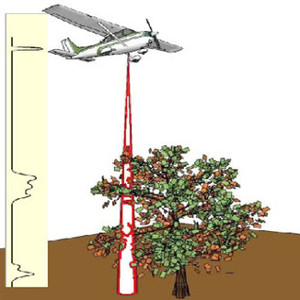
Accurate ground detection in waveform LiDAR signals
Waveform LiDAR data are frequently used to analyze vegetation vertical structure. The majority of LiDAR products (e.g. height, biomass) are dependent on accurate identification of the ground return. Here, we present a new algorithm for ground detection that is considerably more accurate and computationally efficient. Further information: W. Zhuang, G. […]
Read More
RS multi-step classification using intermediate results
A new RS classification algorithm is proposed where classification takes place in multiple steps. Initially, easy to classify pixels are detected, which are then spatially processed to create additional contextual information to assist classification of the more challenging pixels. Further information: G. Mountrakis, L. Luo (2011). Enhancing and replacing spectral […]
Read More
Wildlife vehicle collisions: A review of geographic models
Collisions of vehicles with wildlife pose significant dangers for humans and animals. This review examines geographic models used in collision mitigation along with suggestions for future work. Further information: K. Gunson, G. Mountrakis, L. Quackenbush (2011). Spatial wildlife-vehicle collision models: A review of current work and their application to transportation […]
Read More
Urban growth prediction models: Challenges moving forward
UGPMs have allowed us to understand the mechanisms behind urban sprawl. This review goes beyond summarizing the state of the art by including a survey on barriers perceived by practitioners in wide spread UGPM adaptation. Further information: D. Triantakonstantis, G. Mountrakis, (2012). Urban growth prediction: A review of computational models […]
Read More
Hurricane Katrina flooding disproportionately affected African American neighborhoods
Integration of satellite images with Census data studied the flooding during hurricane Katrina in 2005. Results indicate that flooding was concentrated on predominantly African American communities. Further information: R. Khatami, G. Mountrakis (2012). Implications of Classification Methodological Decisions in Flooding Analysis from Hurricane Katrina. Remote Sensing, 4(12), 3877-3891. [4.9MB pdf]
Read More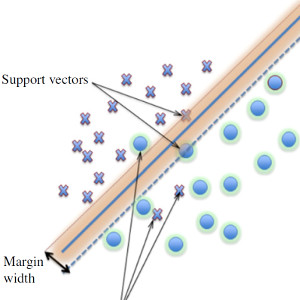
Support Vector Machines in RS problems
Support Vector Machines are a promising family of classifiers due to their low requirements of training samples, fast training times and relative high accuracy. In this review we discuss benefits and limitations and provide a collective summary of applications in the remote sensing field. Further information: G. Mountrakis, J. Im, […]
Read More
Fifteen years of published land cover classifiers
A meta-analysis covered fifteen years of published works in the top five RS journals. We identified the added value of different pre-processing techniques and the relative benefits of popular classification methods to guide practitioners and researchers. Further Information: R. Khatami, G. Mountrakis, S. Stehman (2016). A meta-analysis of remote sensing […]
Read More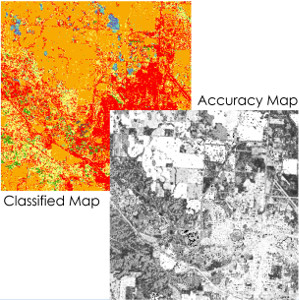
Creation of pixel-based accuracy maps for RS classification
Detailed accuracy maps communicate effectively limitations of RS classification products. Using interpolation methods in the spectral space we demonstrate that per-pixel accuracy predictions are feasible and they offer a better representation of accuracy variability in a given scene. Further information: R. Khatami, G. Mountrakis, S. Stehman (2017). Mapping per-pixel predicted […]
Read More